QR-SAM Test Fired
India successfully test-fired its Quick Reaction Surface to Air Missile (QRSAM) system on 23 December 2019, from the Integrated Test Range (ITR) at Chandipur near Balasore. The missile, developed by the Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO), was flight-tested with the full configuration in deployment mode intercepting the target mid-air, meeting the mission objectives. The entire event was monitored by ground telemetry systems, range radar systems and electro-optical tracking system. The system is likely to be inducted into service by 2021.
This was the seventh test-firing, in which two missiles were test-fired. Both the firings were successful, and with this, the development of the missile was declared complete. The first test-firing of the missile took place on 4 June 2017 from Chandipur. Over 100 scientists have worked on the project and the test on 23 December marked the successful conclusion of their joint efforts. The earlier tests were done for testing different design and performance parameters and barring the third test, all were successful. The sixth test was conducted on 4 August 2019 from a mobile truck-based launcher.

The QR-SAM weapon system has the capability to search and track targets while on the move. It comprises a fully automated command and control, active array battery surveillance radar, active array battery multifunction radar and launcher. Both the radars are four-walled having 360-degree coverage with a search on move and track on move capability. This missile is an all-weather, all-terrain surface-to-air missile equipped with electronic countermeasures against jamming by aircraft radars. The missile can be mounted on a truck and is stored in a canister. QRSAM uses solid-fuel propellant and has a range of 25-30 km. It is equipped with a midcourse inertial navigation system with a two-way data link and a DRDO-developed terminal active seeker. This marks an important step in India’s capacity to manufacture high technology defence systems indigenously.
FAREWELL MIG 27
On 27 December, the last of the MiG 27 Squadrons were phased out in a ceremony held at the Jodhpur Air Force station, marking yet another epoch in the history of the IAF. The MiG 27 first came into operational use by the IAF in 1984, and over a period of time, seven squadrons were raised. Over the last 35 years, the MiG 27 squadrons have made an immense contribution to the nation, both during peace and war. The fleet earned glory during the Kargil conflict when it delivered rockets and bombs with precision on enemy positions. It was the first time that these single-engine fighters were used to attack targets at high altitude.
With the phasing out of the last squadron of the MiG 27, the IAF inventory has come down to just 30 squadrons from the required 42 combat squadrons to fight a two-front war. The IAF operated 165 MiG-27 fighters, around 40 of which were upgraded by state-owned Hindustan Aeronautics Limited from 2005 onwards. The phasing out began a few years ago. The MiG 27 has been the backbone of the ground attack fleet of IAF. The upgraded variant of this last swing-wing fleet has been the pride of IAF since 2006. All the other variants such as MiG-23 BN and MiG-23 MF and the pure MiG-27 have already retired from the IAF. HAL gave the aircraft an avionics upgrade, superior navigation systems and improved targeting accuracy with the integration of Israeli and Russian technology.

INDIA-US 2+2 DIALOGUE
The second round of the “2+2” dialogue between India and the United States — involving the foreign and defence ministers of the two countries have provided a forward-looking vision for India-US strategic partnership and placed the relationship between the two countries on a stronger footing. The Ministers noted that the deepening strategic partnership between India and the United States is rooted in shared values of freedom, justice, human rights and commitment to the rule of law. The meeting was held in Washington on 18 December 2019. The inaugural 2+2 dialogue was held in New Delhi in 2018.
During the Washington “2+2” dialogue, both sides committed to further deepen military-to-military cooperation, including between the Indian Navy and the US Navy Fleets under US Indo-Pacific Command, Central Command, and Africa Command and also to expand similar cooperation between their respective Armies and Air Forces. A number of other initiatives to enhance military-to-military cooperation were also agreed upon.
A highlight of the dialogue was the conclusion of the Industrial Security Annex (ISA). This will deepen industry collaboration, enable the release of more advanced technology and information to India and help make India part of the global supply chain in the defence sector. Defence Minister Rajnath Singh stated that the conclusion of the ISA with the US will provide the necessary framework for pursuing the co-development and co-production linkages in the defence manufacturing centre. According to Nisha Desai Biswal, President, US-India Business Council, “…the most important outcome was the signing of the ISA. I believe the ISA signing will make it possible to deepen the industry collaboration and to enable the release of more advanced technology and information to Indian industry that is working in partnership with US industry on a number of these projects…If we want to build a defence supply chain in India and have India be a global manufacturer and supplier with the US products and technologies, I think the ISA is incredibly important”.
During the 2+2 Dialogue, priority initiatives were also identified for execution under the Defence Technology and Trade Initiative (DTTI) programme and a standard operating procedure for this process was concluded. This will provide momentum to collaboration between the private defence industries of both India and the US. The two sides also agreed to move forward in their engagement in the area of defence innovation.
Another important highlight of the dialogue was the reiteration of the commitment to a free, open, inclusive, peaceful, and prosperous Indo-Pacific region. Appreciating the convergence in their respective Indo-Pacific visions, the ministers reiterated their support for ASEAN centrality, rule of law, freedom of navigation and overflight, peaceful resolution of disputes, and sustainable and transparent infrastructure investment.

![]()
They reaffirmed that closer India-U.S. cooperation is instrumental in promoting security and prosperity in the broader Indo-Pacific region and beyond. This was perhaps aimed at countering the increasing Chinese intransigence in the South China Sea and the increasing presence of the Chinese navy in the Indian Ocean.
It is possibly the clearest enunciation that the Narendra Modi government will seek new partners to further its national interest and to preserve peace and stability in the Indian Ocean Region—especially to ensure the security of its energy needs. There is thus a convergence of interests with the US in this region such as the US tilt to the Pacific and its search for allies there, the decreasing importance of West Asia as a source for US energy needs and US interests in containing China. Given India’s centrality in the Indian Ocean and its growing economic clout, it makes sense for the US to have India as a partner in this venture along with Japan and Australia. The quad (India, US, Japan and Australia) grouping, though currently pitched at a lower scale has the potential to become a viable force for ensuring free, open and unhindered passage of the sea lanes of communication and as a reflection of US concerns, the new term “Indo-Pacific” has replaced the earlier coinage for the Pacific area. The coming years will hence see much greater cooperation between the US and India on multiple fronts, based on the security needs of both countries.
SARVATRA BULLET PROOF JACKET
A level 4 bulletproof jacket has developed at the college of military engineering in Pune which can provide full-body protection against sniper rifle bullets. The jacket was developed by Major Anoop Mishra, who was awarded the Army Design Bureau Excellence Award for this achievement by the COAS General Bipin Rawat

The officer stated that the jacket was developed to foil Pakistani sniper attacks on the line of control. He said that the jacket has been tried and tested by the Infantry at their test facilities. The Indian Army is expected to issue a tender for these full-body protection bulletproof jackets which would be produced by one of the selected Indian defence industry partners.
In 2014, Army Major Anoop Mishra was hit by a bullet while serving in Kashmir valley. The bullet hit his bulletproof jacket which saved his life, but the trauma he went through provided the stimulus to design and develop a jacket with full-body protection against sniper fire. The project was sanctioned in June 2017, initially as a Level IIIA soft body armour suit, but was subsequently revised to include a Level IV hard armour panel insets.
DEFENCE ATTACHE IN MADAGASCAR
In a bid to counter China’s growing influence in the Indian Ocean Region, India has for the first time appointed a Defence Attache to Madagascar. The move is seen as consolidating India’s presence in the western Indian Ocean, a region where China continues to rapidly expand its presence both economically and militarily. The attache in Antananarivo is also expected to focus on nearby islands such as Comoros and France’s Reunion, amongst others.The move comes after India signed a memorandum of understanding with Madagascar in 2018 under which it aims to train some of the defence personnel of the island country.
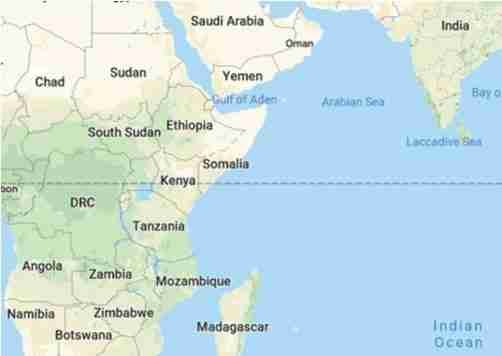
This followed MEA’s decision earlier this month to bring the countries in the region under one umbrella, namely the Indian Ocean Region Division which handles Sri Lanka, Maldives, Mauritius and Seychelles. This division will now also deal with Madagascar, Comoros and the French Reunion in the western Indian Ocean. With this, the aim is to make strategic inroads into the western Indian Ocean, a region China sees as its gateway to Africa. Both Madagascar and Comoros have also expressed interest in involving the Indian Coast Guard in HADR missions as both the Island nations are often hit by cyclones.
EXERCISE MITRA SHAKTI

The seventh edition of Exercise MITRA SHAKTI- 2019 aimed at enhancing interoperability and operational efficiency amongst the armies of both India and Sri Lanka when deployed as part of United Nations peacekeeping forces was carried out in the first week of December at Aundh Military Station, Pune. It aimed at building and promoting positive relations between the armies of India and Sri Lanka through a focus on sub-unit-level training on counter-insurgency and counter-terrorism operations in an urban and rural environment under United Nations mandate. The joint training exercise signifies the strength of India-Sri Lanka relations in the field of military cooperation and engagement, which is vital for refining the interoperability and operational preparedness.
JAWANS TO GET TWO YEARS SERVICE EXTENSION
In a bid to retain trained manpower for a longer duration, the Army has given its approval to extend the services of soldiers by two years. As per a senior defence official, “We have given an across the board approval to raise the minimum tenure of retirement for all the soldiers by two years. The file has been sent to the government for final consent”. Once approved, jawans will serve for a minimum tenure of 17 years. This will reduce the cost of training new jawans along with the problem of providing them reemployment. Of the one million-plus jawans serving in the army, almost 60,000 retire every year. For two years, the forces can thus also
save on recruiting new manpower. This will also reduce the overall pension bill.
 In addition to the above, a study has been launched to identify arms and services in which soldiers can be retained for even longer periods. There are various trades and branches within the Army where it is proposed to allow individuals in those trades to serve up to 50 years. This will subsequently be enhanced to 54 years in phases with minimum disturbance to intake and training quality thereafter. The age limit will be kept 50 years for four-five years and then will be raised to 52. It will be then raised to 54 after another pause of four-five years. The study has been forwarded to the Army Commanders and the Director Generals of various services and directorates for their comments.
In addition to the above, a study has been launched to identify arms and services in which soldiers can be retained for even longer periods. There are various trades and branches within the Army where it is proposed to allow individuals in those trades to serve up to 50 years. This will subsequently be enhanced to 54 years in phases with minimum disturbance to intake and training quality thereafter. The age limit will be kept 50 years for four-five years and then will be raised to 52. It will be then raised to 54 after another pause of four-five years. The study has been forwarded to the Army Commanders and the Director Generals of various services and directorates for their comments.
PAKISTAN BUYING CHINESE HOWITZERS
The Pakistan Army has inked a deal with China Northern
Industries Corporation (NORINCO) to procure 236 SH-15 Howitzerartillery guns. These Howitzers are being procured with transfer-of-technology (ToT) clauses. A contract to that effect was signed in June 2019 worth USD 512 million, of which the first instalment of USD 20 million has been paid in November. NORINCO will also supply adapted ammunition to Pakistan Army.

The SH-15 is a truck-mounted artillery system fitted with a 155 mm gun-howitzer. The Howitzer has probably modified ordnance of an AH-2 155 mm/L52 howitzer and is compatible with all standard 155 mm NATO ammunition, as well as indigenous ammunition developed by NORINCO. This howitzer thus can use a wide variety of different ammunition. Capable of both direct and indirect fire, the maximum range is reportedly up to 53 km with a rocket-assisted V-LAP projectile. In addition, this artillery system can use indigenous precision-guided munitions, based on the Russian Krasnopol laser-guided projectile technology. These have a range of 20-25 km.
This truck-mounted howitzer has built-in ammunition boxes and carries various rounds with associated charges. Before firing, two large spades are lowered to the ground at the back to provide a more stable firing platform. The maximum rate of fire is assessed to be around 4-6 rounds per minute.

